

Received date: 2021-02-03
Revised date: 2021-04-23
Online published: 2022-10-13
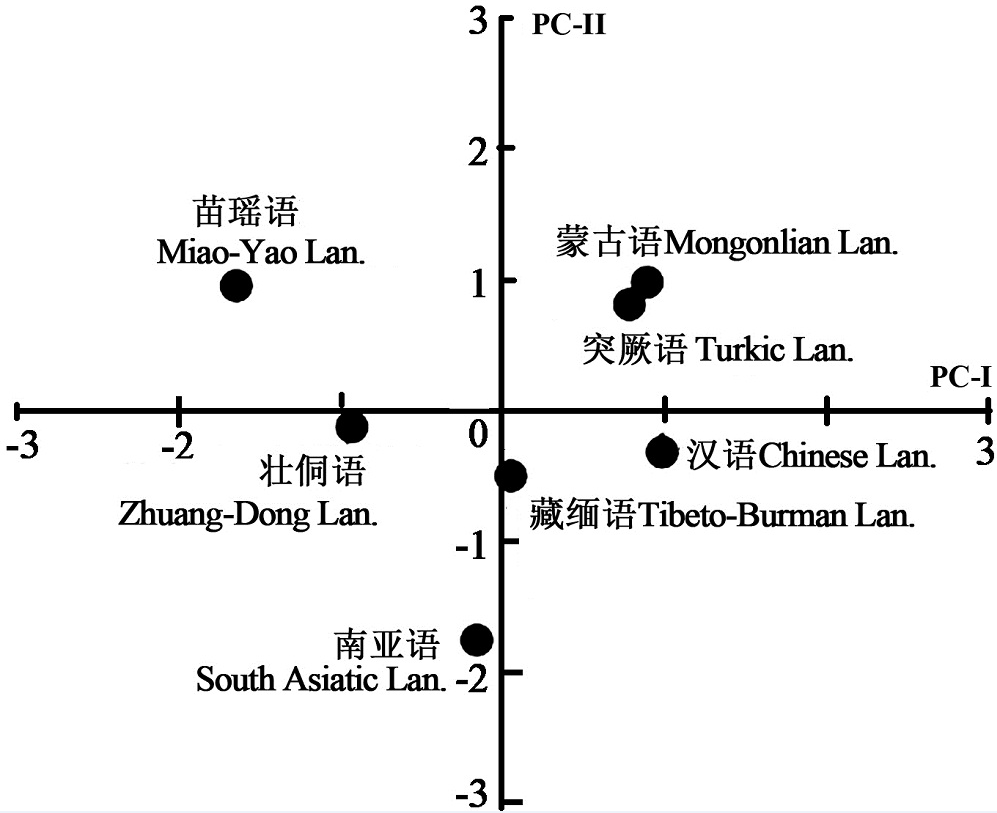
This paper is based on the statistical analysis of 12 indices of the human body of 63452 Chinese people aged from 18 to 97 years old, and the morphological characteristics of Chinese people at present were obtained. Studies have found that overall body type of Chinese people are generally long torso, mid-shoulder, mid-pelvic, and mid-leg type. Men have a mid-chest shape, and women have a wide-chested shape. As their age increase, the upper body of Chinese appears shorter, the ratio of upper body to lower body is smaller, the chest becomes wider, the lower part of torso appears wider, and the legs appear longer. Compared with the southern ethnic groups, the Mongolian and Turkic ethnic groups have a stronger body, a thicker chest, a taller upper body, shorter upper limbs, and a relatively narrower upper part of the torso (shoulder), and a wider lower part of torso (pelvis). The ratio of the length of the upper limbs to the length of the lower limbs is smaller. The study also found that compared with women of the same height, men’s upper limb length and lower limb length are generally smaller than women, and women have a greater sitting height value than men. Compared with the length of the torso, women do have shorter legs than men. Compared with Chinese men and women the same lower body length, the sitting height of women is larger than that of men. In the case of the same height, the sitting height of the Chinese is larger than that of the Eurasian and African races. That is, they have a higher upper body height.
Key words: Body index; China; Age; Ethnic groups; Anthropometry
Yonglan LI , Lianbin ZHENG . Body indexes of the Chinese population[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2022 , 41(05) : 848 -861 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2021.0059
| [1] | 郑明霞, 郑连斌. 中国17个人群体部指数的多元分析[J]. 解剖学研究, 2005, 27(2): 129-132+135 |
| [2] | 涂春景, 江崇民, 蔡睿. 新疆克拉玛依市维吾尔族和汉族成年人体部体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2017, 36(3): 370-379 |
| [3] | 李咏兰, 郑连斌, 旺庆. 鄂尔多斯蒙古族的体部特征[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2015, 6: 723-727+736 |
| [4] | 徐昶楠, 孙贵龙, 丁如佳, 等. 基诺族聚居区儿童身体形态指标变化分析[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019, 40(4): 563-566+571 |
| [5] | 王璐璐, 徐培培, 许娟, 等. 6-18岁学龄儿童生长发育评价指标综述[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2019, 40(4): 627-631 |
| [6] | 季成叶. 中国学龄儿童青少年超重、肥胖筛查体重指数值分类标准[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2004, 2: 97-102 |
| [7] | Luis Eduardo DMT, Tania RG, Yeny PCF, et al. Potential for body mass index as a tool to estimate body fat in young people[J]. Enfermería Clínica (English Edition), 2021, 31(2): 99-106 |
| [8] | Hossain S, Biswas RK, Hossain MA. Body mass index of women in Bangladesh: comparing Multiple Linear Regression and Quantile Regression[J]. Journal of Biosocial Science, 2020, 1: 1-19 |
| [9] | Gabriela V, Nathalia A, Mariana F, et al. SUN-252 Comparison of Sitting Height/Height Ratio for Age in Children with Short Stature Caused by Defects in Growth Plate Genes[J]. Journal of the Endocrine Society, 2019, 3(s1), SUN-252 |
| [10] | Martin R, Saller K. Lehrbuch der anthropologie[M]. Stuttagart: Veb Gustav Fischer Verlag, 1956 |
| [11] | 吴汝康, 吴新智, 张振标. 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984, 103-112 |
| [12] | Bogin B, Varela-Silva MI. Leg Length, Body Proportion, and Health: A Review with a Note on Beauty[J]. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2010, 7: 1047-1075 |
| [13] | 唐锡麟. 儿童少年生长发育[M].译者:王培英. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1991, 78-79 |
| [14] | 傅世侠, 张昀. 生命科学与人类文明[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1994, 61-62 |
| [15] | 雅•雅•罗金斯基, 马•格•列文. 人类学[M]. 北京: 警官教育出社, 1993, 65-66+73-75 |
| [16] | Lin YC, Wang MJ, Wang EM. The comparisons of anthropometric characteristics among four peoples in East Asia[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2004, 35(2): 173-178 |
| [17] | Dewangan KN, Kumar GVP, Suja PL, et al. Anthropometric dimensions of farm youth of the north eastern region of India[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2005, 35(11): 979-989 |
| [18] | Moss S, Wang Z, Salloum M, et al. Anthropometry for WorldSID, a World-Harmonized Midsize Male Side Impact Crash Dummy[R/OL]. Office of Scientific & Technical Information Technical Reports, doi: 10.4271/2000-01-2202 |
| [19] | Jung SG, Kim GH, Roh WJ. Comparisonof basic body dimension between Korean and American for design application[J]. Korean Society of Basic Design and Art, 2000, 1(2): 65-75 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |