

A preliminary report of the excavation of Chaoyang Cave 2 in Jizhou County, Tianjin City
Received date: 2023-10-15
Revised date: 2023-12-05
Online published: 2024-04-02
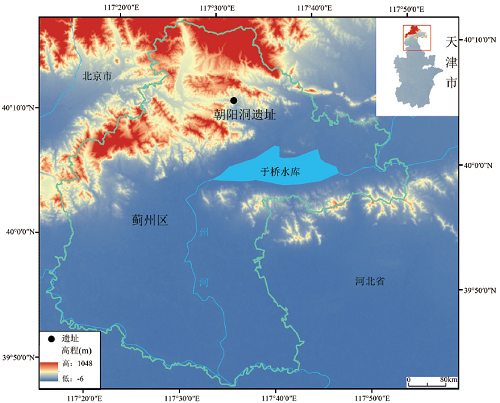
Jizhou District, located in the northern part of Tianjin, contains all the Paleolithic sites found in Tianjin, which is of vital importance for research on ancient human activity in the region, so it can be called as the cradle of Paleolithic archaeology in Tianjin. In May 2015, an archaeological survey of Paleolithic sites in Jizhou, Tianjin was conducted by a team led by the Protection Center of Cultural Heritage in Tianjin and School of Archaeology Jilin University.More than ten open-air Paleolithic site was newly discovered in this survey. The Chaoyang Cave site, sitting in the northern mountainous region of Jizhou District, was discovered during this survey and was formally excavated from July to September 2019, making it the first excavated Paleolithic cave site in Tianjin. The site consists of Cave 1 and Cave 2, with pottery, stone artifacts and animal fossils unearthed from Cave 1 and stone artifacts unearthed from Cave 2. This article only studies the stone artifacts unearthed from Cave 2.The cultural deposits is about 4 m thick. The stratigraphy of the site consisted of 4 layers (from top to bottom): Layer 1, humus soil layer(containing angular gravel); Layer 2, Clay layer(containing angular gravel); Layer 3, cultural deposits including artifacts; and Layer 4, bedrock (limestone). Stone artifacts from Cave 2 were excavated form Layer 3. A total of 66 stone artifacts were collected from deposits and include flakes and retouched tools. Raw materials were mainly High-quality flint, probably selected from river gravels. Flakes were generally micro to small in size. Hard-hammer percussion was more common than bipolar percussion. The type of tools is simple, including only scrapers and notch, whereas most of their blanks are flakes. Technological analysis suggests that flake-tool production system based mainly on small flake blanked scrapers. The small number of stone artifacts at the site, including only stone flakes and a very small number of retouched tools, and the absence of other types of relics, suggest that Chaoyang Cave 2 was a temporary camp. The dating results of Cave 2 are not yet available but based on the analysis of the stone artifacts and sediments, together with comparative studies with other Paleolithic sites and localities in Tianjin, it is assumed that the date could be not later than the Upper Paleolithic. Research on the Chaoyang Cave site is important for exploring the relationship between different stone-tool industries in Tianjin, improving the chronological sequence of the Paleolithic and revealing early human behaviors in the area.
WEI Tianxu , WANG Chunxue , ZHANG Xuewei , WANG Jiaqi , SHENG Lishuang . A preliminary report of the excavation of Chaoyang Cave 2 in Jizhou County, Tianjin City[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024 , 43(02) : 314 -320 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0028
| [1] | 盛立双. 初耕集—天津蓟县旧石器考古发现与研究[M]. 天津: 天津古籍出版社, 2014 |
| [2] | 盛立双, 王春雪, 甘才超, 等. 天津蓟县2015年旧石器考古调查报告[J]. 边疆考古研究, 2018, 2: 27-39 |
| [3] | 蓟县志编修委员会. 蓟县志[M].天津: 南开出版社, 天津社会科学院出版社,1991 |
| [4] | 卫奇. 《西侯度》石制品之浅见[J]. 人类学学报, 2000, 19(2): 85-96 |
| [5] | 王春雪, 盛立双. 天津蓟县太子陵旧石器地点调查简报[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(1): 37-44 |
| [6] | 王春雪, 盛立双, 周振宇, 等. 天津蓟县东营坊遗址出土的石制品[J]. 人类学学报, 2015, 34(1): 14-20 |
| [7] | 王春雪, 盛立双. 天津蓟县小平安旧石器地点调查简报[J]. 北方文物, 2013, 4: 3-6 |
| [8] | 宋家兴, 魏天旭, 李万博, 等. 天津市蓟州区三处旧石器地点调查简报[J]. 北方民族考古, 2023, 1: 1-17 |
| [9] | 王春雪, 李万博, 陈全家, 等. 天津蓟县杨庄西山旧石器地点发现的石制品[J]. 边疆考古研究, 2017, 1: 1-12 |
| [10] | 纪烈敏, 刘健, 张俊生. 天津蓟县青池遗址发掘报告[J]. 考古学报, 2014, 2: 195-242 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |