

Physical characteristics of the Huangyi Va people in China
Received date: 2023-11-27
Revised date: 2024-02-03
Online published: 2024-08-13
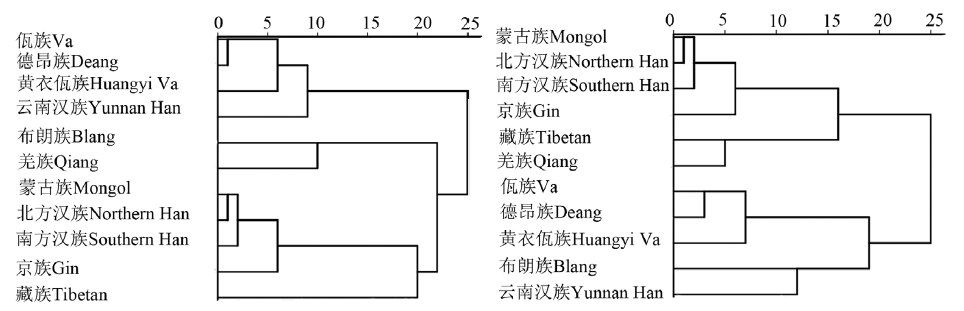
The Va people are distributed in the border area between China, Myanmar and Thailand, and their language belongs to the Mon-Khmer language group, which is divided into Va Va, A Va and Baraoke Va. In order to explore the physical characteristics of the Huangyi Va ethnic group in China, the research team measured the head, face and body parameters of 325 adults (127 males and 198 females) in Dazhai Village, Mengjian Township, Lincang City, Yunnan Province in 2023. Physical index and classification were calculated and analyzed by Excel and SPSS. The results are as follows: The crease rate of eyefold of the upper eyelid of male and female was higher (89.8% in male and 93.4% in female), and the mongoloid fold rate was lower (18.9% in male and 16.2% in female). The opening height of eyeslits was mainly medium, the direction of eyeslits was mainly medium, the maximum diameter of nostrils was mainly transverse, the nasal profile was mainly straight, and the alae nasi breadth was mainly wide. The lobe types was round, the zygomatic projection was tiny, and thickness of lips was middle. There were significant differences between men and women in 47 parameters such as head length, head breadth and minimum frontal breadth, which cresta iliaca breadth and hip circumference were greater in women than in men, and the other 45 parameters were greater in men than in women. According to the occurrence rate of index classification, it can be concluded that the men and women of Huangyi Va are mesocephaly, hypsicephalic, acrocephalic, mesorrhiny, medium trunk, wide chest, wide shoulder and wide crista iliaca, and the short stature type is the highest. Cluster analysis shows that the Huangyi Va ethnic group is close to Va and Deang. The principal component analysis showed that compared with the other 10 ethnic groups, the nose breadth, lip height, mouth breadth and interocular breadth of the Huangyi Va male were larger, and the face breadth and head length of the Huangyi Va male were smaller. The nose breadth, lip height, mouth breadth, interocular breadth, head length of the Huangyi Va female are at a high level.The morphological facial height and face breadth of Huangyi Va female is at a low level. This is closely related to genetic factors, living environment, eating habits and so on. The Huangyi Va adults belong to the physical characteristics of the southern ethnic groups.
Key words: Huangyi Va; Head and face; Body; Anthropometry; Physical characteristic
LYU Jingyi , XIAO Yao , YU Keli , CHENG Zhi , NIE Haobo , GAO Xinying , YAO Yuetong , BAO Jinping , ZHENG Lianbin , ZHANG Xinghua . Physical characteristics of the Huangyi Va people in China[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2024 , 43(04) : 549 -560 . DOI: 10.16359/j.1000-3193/AAS.2024.0040
| [1] | 周家瑜. “黄佤”:独特的佤族支系[J]. 今日民族, 2007, 9: 21-28 |
| [2] | 周家瑜, 李发荣. “过渡礼仪”视野下的黄衣佤族丧葬习俗解读[J]. 怀化学院学报, 2012, 31(9): 10-13 |
| [3] | 李学明. 佤族服饰简介[J]. 今日民族, 2010, 4: 22-23 |
| [4] | 周家瑜. 宗教对话视野下制度化宗教与民间信仰的并存与互融——以云南省勐简大寨黄衣佤族宗教信仰情况为例[J]. 民族论坛, 2011, 271(6): 43-45 |
| [5] | 杨茂芳. 探访耿马勐简“黄衣阿佤”[J]. 云南档案, 2017, 7: 32-36 |
| [6] | 郑连斌, 陆舜华, 于会新, 等. 佤族的体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2007, 26(3): 249-258 |
| [7] | 于会新, 郑连斌, 陆舜华, 等. 佤族成人Heath-Carter法体型研究[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 28(2): 18-22 |
| [8] | 王雅萱, 李珊, 宇克莉, 等. 云南省佤族、拉祜族与哈尼族成人的体成分比较研究[J]. 天津师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 39(3): 76-80 |
| [9] | 郑连斌, 陆舜华, 张兴华, 等. 中国图瓦人体质特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2013, 32(2): 182-192 |
| [10] | 席焕久, 陈昭. 人体测量方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010, 145-156 |
| [11] | 宇克莉, 杜慧敏, 贾亚兰, 等. 布朗族的体质特征[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2017, 40(5): 574-579+602 |
| [12] | 廖彦博, 李坤, 郑连斌, 等. 广西京族体质人类学研究[J]. 人类学学报, 2010, 29(1): 100-102 |
| [13] | 李咏兰, 宇克莉, 张兴华, 等. 藏族的体质类型和人种学特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(4): 698-711 |
| [14] | 李晶, 李珊, 宇克莉, 等. 羌族的体质特征[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2018, 41(4): 440-445+486 |
| [15] | 李咏兰, 郑连斌. 中国蒙古族体质人类学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 100-180 |
| [16] | 郑连斌, 李咏兰, 席焕久, 等. 中国汉族体质人类学研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 20-22 |
| [17] | 郑连斌, 宇克莉, 包金萍, 等. 云南汉族体质特征[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 35(5): 703-718 |
| [18] | 杨竹芬, 苏红斌. 佤族、布朗族、德昂族的身份认同研究[J]. 黑龙江史志, 2013, 294(5): 43-45 |
| [19] | 李咏兰, 张兴华, 孙泽阳, 等. 中国人的头面部形态特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2022, 41(3): 450-462 |
| [20] | 李祎, 赵雯婷, 李丹, 等. EDARV370A对新疆维吾尔族人群面部及耳朵形态的效应[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(11): 1024-1034 |
| [21] | Kun E, Javan EM, Smith O, et al. The genetic architecture and evolution of the human skeletal form[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6655): eadf8009 |
| [22] | Lee MK, Shaffer JR, Leslie EJ, et al. Genome-wide association study of facial morphology reveals novel associations with FREM1 and PARK2[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): e0176566 |
| [23] | Bonfante B, Faux P, Navarro N, et al. A GWAS in Latin Americans identifies novel face shape loci, implicating VPS13B and a Denisovan introgressed region in facial variation[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(6): eabc6160 |
| [24] | Shaffer JR, Orlova E, Lee MK, et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Multiple Loci Influencing Normal Human Facial Morphology[J]. PLoS Genet, 2016, 12(8): e1006149 |
| [25] | Howe LJ, Lee MK, Sharp GC, et al. Investigating the shared genetics of non-syndromic cleft lip/palate and facial morphology[J]. PLoS Genet, 2018, 14(8): e1007501 |
| [26] | Huang Y, Li D, Qiao L, et al. A genome-wide association study of facial morphology identifies novel genetic loci in Han Chinese[J]. J Genet Genomics, 2021, 48(3): 198-207 |
| [27] | 李红军. 勐简大寨的黄衣阿佤[J]. 今日民族, 2012, 7: 29-31 |
| [28] | 周家瑜. 文化涵化与族群:以“黄佤”族群文化为例[J]. 怀化学院学报, 2008, 27(7): 14-17 |
| [29] | Crognier E. Climate and anthropometric variations in Europe and the Mediterranean area[J]. Annals of Human Biology, 1981, 8(2): 99-107 |
| [30] | Ji Ld, Xu J, Yp Z. Environmental adaptation studies in human populations[J]. Chin Sci Bull (Chin Ver), 2012, 57(Z1): 112-119 |
| [31] | Zaidi AA, Mattern BC, Claes P, et al. Investigating the case of human nose shape and climate adaptation[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2017, 13(3):e1006616 |
| [32] | 李咏兰, 于会新, 张兴华, 等. 中国不同地理分区人群的头面部特征[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(6): 793-806 |
| [33] | Yeo IS, Park JA, Lee HI, et al. Anthropometric Analysis of the Growth Proportions of the Head and Face in Koreans[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2022, 33(1): 333-336 |
| [34] | Pavlica TM, Raki? RS, Bo?i?-Krsti? VS, et al. Secular trend of head and face shape in adult population of Vojvodina (Serbia)[J]. Ann Hum Biol, 2018, 45(4): 330-336 |
| [35] | Lim YC, Abdul Shakor AS, Mohamad N, et al. Head and face anthropometric study for respirators in the multi-ethnic Asian population of Malaysia[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10: 972249 |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |